Ultimate Guide to Financial Projection Tools for Educators
Financial projection tools simplify teaching financial concepts by helping students focus on budgeting, planning, and decision-making without struggling with complex formulas. These tools are particularly useful for K–12 classrooms, allowing students to explore scenarios like revenue forecasting, expense tracking, and break-even analysis through interactive, hands-on learning. Key features to look for include user-friendly interfaces, collaboration options, and education-focused templates.
Highlights:
- Top Tools: Excel for advanced modeling, Google Sheets for group projects, and Consumer.gov for beginners.
- Key Features: Step-by-step guidance, real-time collaboration, and pre-built templates.
- Teaching Tips: Use real-world data, encourage teamwork, and assess logic behind projections.
These tools transform classrooms into active learning environments, helping students connect financial concepts to practical applications.
What to Look for in Financial Projection Tools
When choosing financial projection tools for classroom use, it's important to focus on features that simplify teaching, encourage collaboration, and include templates tailored for learning. These tools should make it easier for educators to teach financial concepts without being bogged down by technical issues. Here are three key features to prioritize:
Simple Interfaces That Work for Teachers
The best tools are designed with user-friendly interfaces that guide students through financial concepts step by step. A good platform creates a "sandbox" environment where students can test ideas - like adjusting pricing strategies or sales channels - without worrying about breaking formulas or losing their progress. For example, the ExEC Financial Projection Simulator offers a visual, interactive experience that helps students grasp financial concepts without requiring advanced accounting skills.
Collaboration and Sharing Features
Modern tools also make teamwork more accessible. Real-time collaboration allows students to turn financial modeling into a group activity rather than an individual task. With the right tool, students can work on different parts of a budget simultaneously, while teachers can monitor their progress and provide feedback directly within the platform. This eliminates the confusion of managing multiple file versions.
For larger classes, tools like Projection Genie provide role-based access, enabling students to work on specific sections while maintaining clear permissions and oversight - a feature particularly useful in bigger group settings.
Templates Designed for Education
Pre-built templates simplify tasks like revenue forecasting, expense tracking, and break-even analysis. These templates not only help students learn but also make grading easier for teachers. As LivePlan highlights:
"When your students use LivePlan, you get business plans in a modern, standardized outline that makes evaluation and grading easy."
For broader applications, such as district-level planning, tools like Projection-Pro align with reporting standards like SACS, ensuring both compliance and the use of professional-grade financial modeling. Frontline's financial planning tools, currently used by over 2,000 school business officials, are another example of how these templates can serve both educational and administrative needs.
sbb-itb-4f1eab7
Financial Projection Tools for the Classroom
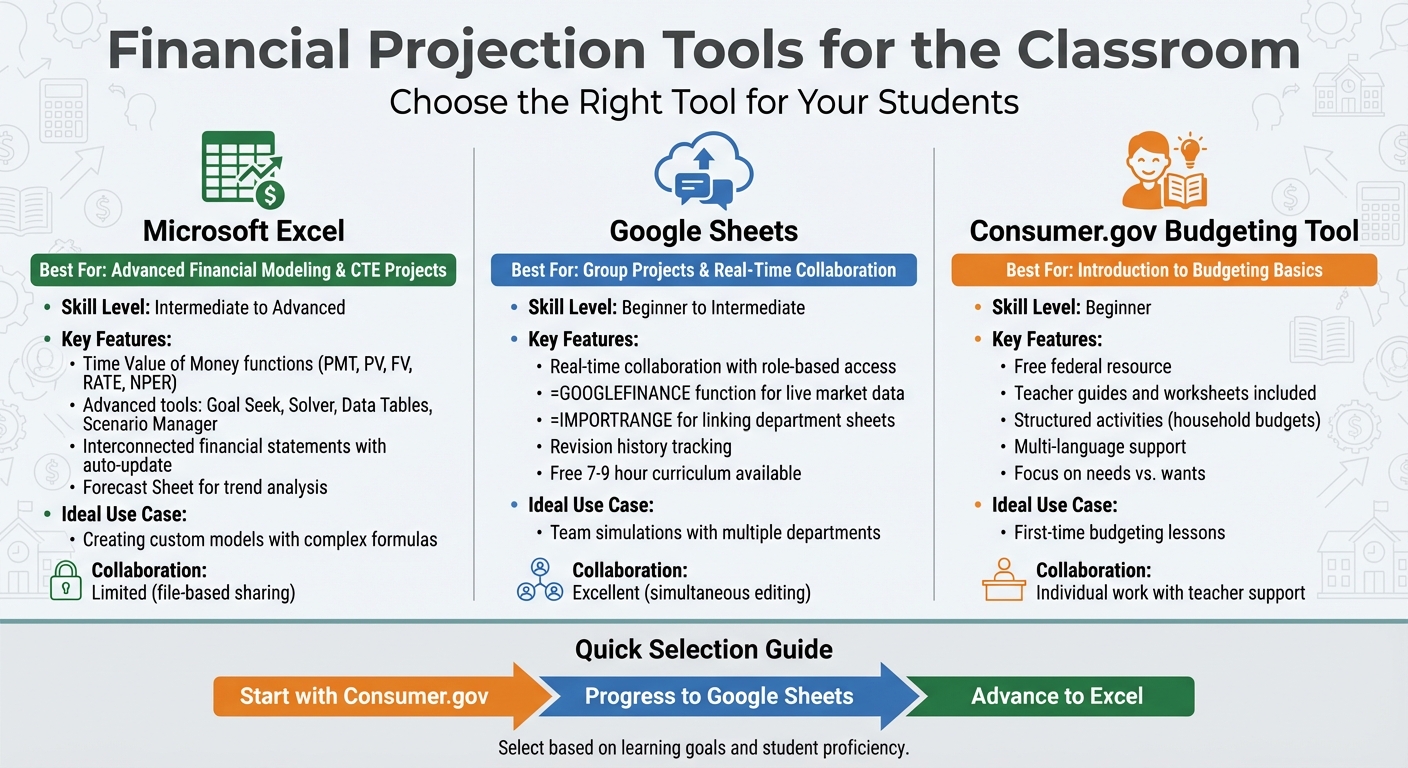
Comparison of Top 3 Financial Projection Tools for Educators
The right tools can turn complex financial ideas into engaging, hands-on learning experiences. Whether teaching basic budgeting or advanced modeling, tools like Excel, Google Sheets, and the Consumer.gov Budgeting Tool cater to a variety of classroom needs.
Microsoft Excel for Custom Financial Models
Excel stands out as a go-to for financial modeling, thanks to its built-in Time Value of Money functions (like PMT, PV, FV, RATE, and NPER) and advanced features such as Goal Seek, Solver, Data Tables, and Scenario Manager. These tools allow students to explore different financial outcomes in depth. Professor Chengping Zhang of George Fox University highlights its educational value:
"Incorporating these tools into finance teaching can help students understand finance concepts intuitively, and bridge the gap between financial theories and real-world applications".
For advanced Career and Technical Education (CTE) projects, students can create interconnected financial statements that auto-update, using balancing formulas to ensure accuracy (e.g., Total Assets - Total Liabilities & Equity = $0). Additionally, Excel's Forecast Sheet tool helps students analyze trends using historical data. These capabilities set it apart from more collaboration-focused tools like Google Sheets.
Google Sheets for Group Projects
Google Sheets shines in group settings, offering real-time collaboration and easy access management through roles like Viewer, Commenter, and Editor. Its revision history keeps group work transparent and organized.
A standout feature is the =GOOGLEFINANCE function, which allows students to pull live stock prices and market data directly into their spreadsheets, connecting lessons to real-world markets. For group simulations, students can use the =IMPORTRANGE function to link data across sheets. For example, different student "departments" (like Marketing, Sales, and Operations) can feed their data into a central Finance team's master sheet. Google also offers a free 7–9 hour curriculum called "Create a Budget in Google Sheets", designed for middle and high school students. It guides students through practical scenarios like budgeting for car loans or vacations.
Consumer.gov Budgeting Tool for Beginners
This free federal resource is perfect for introducing students to budgeting. It provides teacher guides and worksheets that make it easy to teach concepts like balancing needs, wants, and savings.
The platform includes structured activities, such as "Creating a monthly household budget", where students practice managing expenses in hypothetical scenarios before applying the lessons to their own lives. To support diverse classrooms, materials are available in multiple languages. Beyond budgeting, the tool helps students explore the behavioral side of financial management, such as preparing for emergencies and managing money wisely.
How to Use Projection Tools in Your Classroom
Planning Your Financial Projection Lessons
When teaching financial projections, move beyond abstract concepts and formulas. Focus on hands-on activities where students can see how small adjustments impact financial statements in real time. Start with a clear workflow: generate estimates, create monthly projections, analyze cash flow, and perform breakeven analysis. This step-by-step process sharpens their analytical skills and helps them build accurate models.
Align your lessons with specific CTE curriculum goals like revenue forecasting, cost estimation, monthly burn rate, and profitability timelines. This way, students can connect the use of financial projection tools to practical, real-world scenarios. For personal finance classes, consider introducing the PACED decision-making model. This helps students weigh financial choices and understand trade-offs. You can also teach them to categorize expenses (fixed vs. variable) or separate costs like goods sold from operating expenses.
Once the groundwork is laid, bring lessons to life with hands-on activities that mirror real-world financial challenges.
Getting Students Involved with Practice Activities
Divide students into small teams of three or four, with each team member focusing on a specific area like pricing, marketing, or operations. This collaborative setup encourages debate and helps them see how different business functions intersect financially. One entrepreneurship instructor shared their experience:
"The simulation was fun and simple enough for students to get started quickly, but thorough enough to get them thinking. After 30 minutes, they were already tweaking assumptions and reworking their models".
Encourage students to gather real industry data from local startups or e-commerce platforms and incorporate it into their projections. To deepen their understanding, have teams exchange spreadsheets to critique each other’s assumptions, identifying strengths and areas for improvement. For a dynamic classroom experience, use a shared simulator to make real-time updates based on student input. This sparks immediate discussions about how changing variables influence outcomes.
After completing these activities, shift the focus to assessment to reinforce their learning.
Assessing Student Projects with Projection Tools
Once students have practiced, evaluate their projects to solidify their financial reasoning. Focus on the logic behind their numbers rather than presentation. Use rubrics tailored to each stage of the process, such as the realism of estimates, the accuracy of cash flow projections, and the quality of breakeven analysis. Ask students to explain their decisions through short essays or presentations. One instructor noted:
"You could see the learning happening. Students would come up and ask questions like, 'Why do I need such a big building?' And I'd say, 'Exactly - why do you?' They suddenly got it".
Pay attention to how students respond to feedback and revise their models. This iterative "revise-and-learn" process demonstrates their understanding of cause-and-effect relationships in financial planning. To wrap up, have teams present their breakeven analysis, explaining their trade-offs while classmates ask questions or provide suggestions.
Tips for Using Financial Projection Tools Effectively
Matching Tools to Your Curriculum Goals
Choose financial projection tools that align with your students' skill levels and the objectives of your curriculum. For beginners, user-friendly apps can simplify the basics, while advanced Excel models are ideal for in-depth forecasting exercises. Incorporate an iterative approach where students test their assumptions, get feedback from AI-driven simulators, and refine their projections. This hands-on process helps students understand how slight changes - like adjusting pricing or unit sales - can significantly impact financial statements or cash flow forecasts.
AI-powered simulators can also highlight unrealistic assumptions, such as overly optimistic revenue goals, teaching students the rationale behind financial projections. These tools can be used as standalone learning modules, integrated into capstone projects, or assigned as homework to reinforce key concepts.
To make these lessons even more engaging, tie them to examples from actual industries.
Using Examples from Actual Industries
Bring real-world relevance to your lessons by incorporating industry-specific metrics and data that resonate with students. For example:
- In retail, focus on metrics like income per square foot.
- For service-based industries, emphasize factors like headcount and labor costs.
- In telecommunications, highlight market share and customer retention.
Encourage students to research real pricing from local startups or analyze how e-commerce businesses manage operational costs. Using real data in their models not only improves accuracy but also makes the exercise feel more authentic and engaging.
Additionally, leverage management commentary from public companies to ground students' forecasts in reality. For instance, Tesla’s management commentary has helped analysts refine revenue models in response to strategic changes. This example illustrates the importance of validating projections with actual industry insights. You can also have students compare their profit margin estimates to industry benchmarks, like contrasting a local coffee shop’s margins with those of Starbucks, to ensure their models remain realistic.
Using DashK12 Resources for CTE Teaching
DashK12 offers powerful tools and resources to help educators enhance financial literacy instruction. Their online course, The Ultimate Guide to Teaching CTE, equips teachers with the skills needed to integrate financial projections into their curriculum - perfect for those transitioning from industry roles to teaching. The course covers essential strategies and tools, making it easier to incorporate financial concepts into classroom lessons.
DashK12 also provides mentoring and workshops tailored to CTE educators. These sessions offer personalized guidance, helping teachers progress from basic data entry to making data-driven decisions in their classrooms. To learn more, visit DashK12 and explore how their resources can help you build engaging, effective financial projection lessons for your students. By combining these tools with your teaching strategies, you can create impactful CTE curricula that prepare students for real-world financial challenges.
Conclusion
Picking the right financial projection tools can completely change how students approach money and decision-making in business. These tools help students move away from guesswork and toward building realistic models grounded in real data and logical thinking. By experimenting with interactive tools - like tweaking pricing strategies or reducing marketing expenses - students can see how even small changes can impact financial statements and cash flow in big ways.
This hands-on learning approach resonates with seasoned educators.
"Students grasp the cause-effect behind the numbers, ask better questions, and share ideas with each other, transforming your classroom into a lively workshop." - TeachingEntrepreneurship.org
FAQs
What are the advantages of using financial projection tools in the classroom?
Financial projection tools bring a lot to the table for both educators and students, especially when it comes to simplifying and teaching complex financial concepts. These tools break down intricate ideas like financial modeling, helping students grasp how different variables can influence outcomes. The interactive, hands-on nature of these tools also boosts confidence in financial literacy and strengthens practical problem-solving skills.
Beyond just understanding concepts, these tools push students to think critically. They allow experimentation with real-life scenarios, encouraging analysis of results in a way that feels engaging and relevant. Plus, the collaborative aspect makes lessons more interactive and memorable, fostering teamwork and active participation.
For educators, these tools are invaluable for presenting financial data in a clear, digestible format. They help prepare students for the challenges of financial planning and decision-making they’ll face in the future, making them a practical addition to any classroom.
How can educators use real-world data to teach financial projections effectively?
Teaching financial projections doesn't have to be dry or overly theoretical. One way to bring lessons to life is by using interactive tools and real-world data. For instance, financial projection simulators let students plug in realistic numbers, tweak assumptions, and immediately see how those changes affect outcomes. This hands-on method not only sharpens critical thinking but also bridges the gap between classroom theory and practical application.
Another effective approach is incorporating publicly available economic data into lessons. By analyzing current trends and exploring key economic indicators, students can see how external factors - like inflation or interest rates - shape financial projections. This makes abstract concepts feel more tangible and relevant.
By blending interactive tools with real-world examples, educators can equip students with practical skills and a clearer understanding of how financial modeling works in everyday scenarios.
What key features should educators look for in financial projection tools for students?
When selecting financial projection tools, it’s important to focus on options that are easy to use, engaging, and capable of breaking down complex financial ideas into simpler terms. Tools that offer step-by-step instructions, let students build practical financial models, and promote active participation can be especially helpful in the classroom.
Consider tools that leverage AI-powered features to assist students in making precise assumptions while boosting their confidence in financial decision-making. Choosing tools with clear, visual elements and straightforward interfaces can also enhance both understanding and overall engagement.